One of the most frequent questions I get asked by athletes is whether or not it’s ok to eat after a game that finishes late at night. The common misconception is that dinner should not be eaten after a certain time in the evening. This does not apply for athletes! If you are on the couch for the night, then yes, eating dinner earlier may be a good choice. However if you have just finished a tough away game at 10pm it doesn’t matter what time it is, you should be eating after! Sports nutrition recovery principles apply regardless of the time.
Recovery Nutrition
Getting your recovery right helps to set yourself up for the next training session or game, which for most junior basketballers is likely the following day (for example, a late Friday night game, into school basketball the next morning and/or a domestic game in the afternoon). Friday night recovery food is important!
Priorities:
Refuel carbohydrate stores for energy for the next day
Repair muscle damage to reduce soreness and promote muscle growth
Rehydrate by replacing fluid and electrolyte losses
Revitalise by choosing anti-inflammatory, nutrient-dense foods
Key Nutrition Elements:
CARBOHYDRATE - FUEL Rice, quinoa, noodles, potato, sweet potato, pasta, bread
PROTEIN - MUSCLE Meat, fish, chicken, eggs, milk, cheese, yoghurt
HEALTHY FATS - INFLAMMATION Avocado, nuts, fish, olive oil
SODIUM - HYDRATION
ANTIOXIDANTS, VITAMINS, MINERALS Vegetables, fruit, herbs, wholegrains, nuts, seeds
How do we achieve these recovery goals with food? Unfortunately it’s pretty difficult to achieve with the typical take-away options on offer on the drive home.
OPTIONS:
BYO from home - you’ll need a food thermos and a good cooler bag, but with some planning and organisation it can be done!
OR bring some nutrient-dense snacks for immediately post-game then have leftovers ready to heat when you get home.
OR be selective with the type of take-away purchased
The following snack options work well and can be a good start to the recovery process if it’s more than an hour or so before you can get home to eat.
Chicken and salad wrap
Sushi rolls
Pasta or rice dish with chicken or meat and vegetables
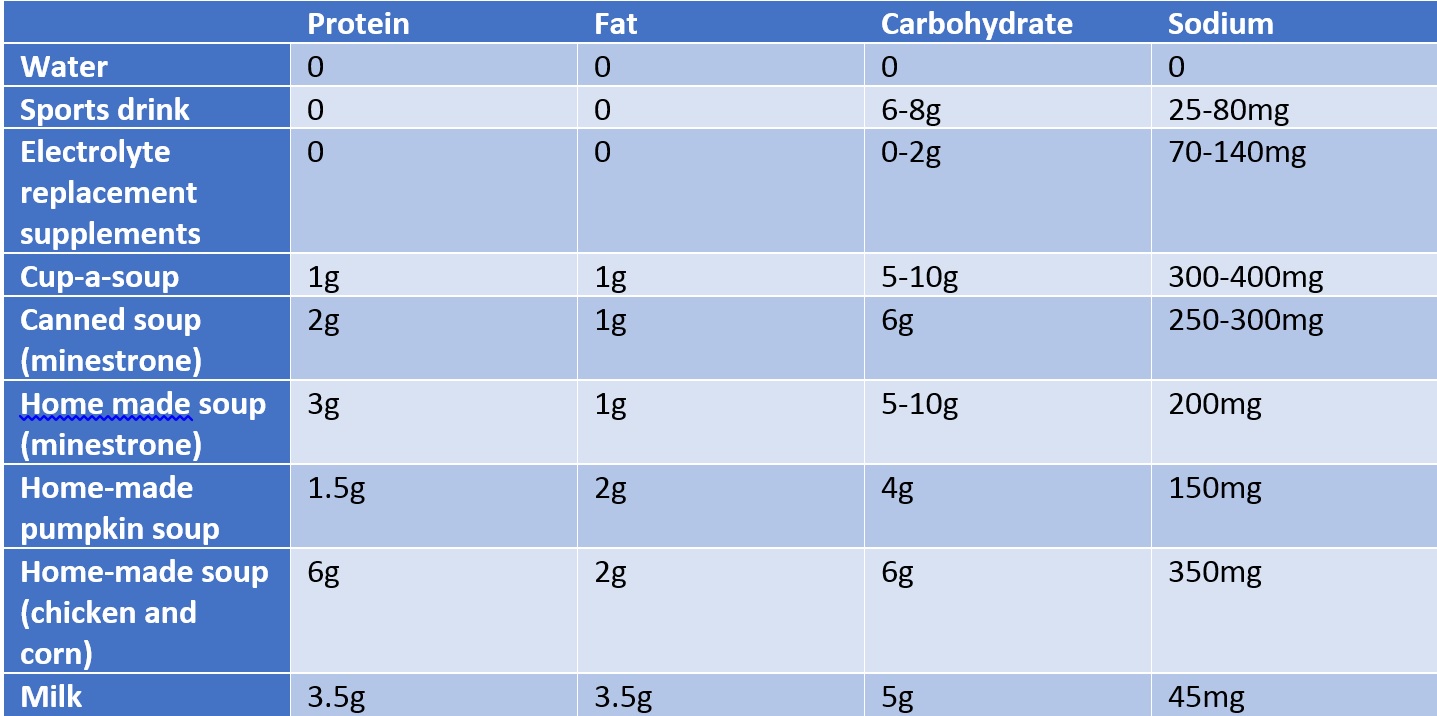
Soup and a cheese roll
High-protein yoghurt with handful of almonds or cashew nuts, plus berries
Vegetable frittata
Home-made sausage rolls
Up’n’Go or Rokeby Farms smoothie and a piece of fruit
Even though some of these need be kept hot or cold, there are lots of storage options out there that will keep food at the right temperature for a few hours. The biggest challenge is being organised and thinking ahead of time. Some options are easier than others!
If you get a good snack in during the car ride, then aim for another small meal or snack once you get home. This should be pre-prepared so it can easily be re-heated quickly. I would recommend to eat straight away on arrival home before a shower, as this allow a little bit of time for digestion before heading to bed.
Example leftovers for recovery:
· Beef and vegetable stir-fry with rice or noodles
· Pasta or lasagne with chicken or lean meat tomato sauce, add vegetables
· Home-made souvlaki or burritos or hamburgers
· Chicken and vegetable curry with rice
Soup with pasta/noodles/rice and meat/chicken/legumes
Even a toasted sandwich with some fruit, or a fruit smoothie can be a great recovery choice for when you haven’t had time to pre-prepare food and everyone is tired. Kids’ appetites can drop as it gets later and they are more fatigued, so it’s important to make sure they do have something to eat and drink before they fall into bed.
Yes, the golden arches do tend to call us when it’s a long drive home from a late rep game, and sometimes (or often) that’s where you end up. However with a little forward planning you can put in place some strategies that become habit for post-game nutrition to help improve energy levels and performance for the rest of the weekend.
Lisa has worked with NBL teams Melbourne United and South East Melbourne Phoenix over 10 years and currently works with Basketball Victoria junior high performance programs. She also has two very active children who play a lot of sport, including basketball.